

The negative charge that is flowing in one direction is equivalent to the positive charge flowing in the opposite direction. The current that is flowing inward is carried by the electrons that are flowing outwards. The anode acts as a negatively charged terminal in the galvanic cell or in the discharge battery as the current flows into the cell through the cathode. In addition, an anode can be a wire or a plate having an excess positive charge. Whereas, in an electrolytic cell, it is given as positive. If we consider a galvanic cell, the anode exhibits a negative nature, and mostly the electrons move towards the external part of the circuit. Then, these electrons move up and into the driving circuit. In general, at an anode, anions, or negative ions, due to their electrical potential, tend to react and give off the electrons. The material that is needed to be plated with pure metal is attached to the cathode and becomes part of the cathode in the solution.Īn anode in electrochemistry is defined as the point where oxidation reaction takes place. The anode of the galvanic cell releases electrons that reach the cell through the circuit wire cathode.Įlectroplating Metal Cathode (Electrolysis) : Once the metal ions are reduced, they form the pure metal surface on the cathode. It is completely connected to allow the circuit to be completed. Galvanic cell : Cathode acts as a positive electrode in the galvanic cell. While considering the relative reducing power of the two redox reactions, the one that makes the most reducing species is more cathodic as compared to the other that itself get reduced easily. The pure metal or hydrogen gas from the metal ions are the result of the reduction at the cathode. In general, a cathode is flagged as "cold" if it emits more electrons than the ones generated by thermionic emission alone.Įlectrolytic cell : In an electrolytic cell the negative polarity appears at the cathode. A cathode that is heated in the presence of a filament to emit electrons using thermionic emission is called a hot cathode, whereas the cold cathodes are not heated with any filament. The flow of current in the interface of the cathode is actually the flow of electrons from the surface of the cathode to the solution.Īlso, a cathode is said to be either a cold cathode or a hot cathode. However, it can also be positive similar to the case of a galvanic cell where the chemical reaction tends to the generation of electrical energy. Here, the cathode is negative due to the electrical energy that is supplied to the cell, which results in the decomposition of chemical compounds. In an electrochemical cell, this is common. When we speak about the cathode in chemistry, it is said to be the electrode where the reduction takes place. The pictorial representation of both cathode and anode is given below. He adapted the words from the Greek word (named, kathodos), 'way down' or 'descent.' William had consulted with Michael Faraday in coining the terms. The terms Cathode and Anode were finalized in 1834 by William Whewell. In the same way, an anode can be described as an electrode from which the current enters into the polarized electrical device. A cathode is an electrode from which the current exits a polarized electrical device. Both these terms can be defined by the flow of current.
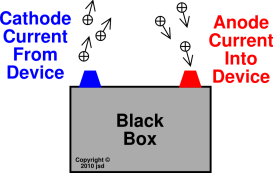
Let us discuss what cathode and anode exactly mean. Electrodes consist of two major points called cathode and anode, which describe the direction of the flow of current. In other words, an electrode can be defined as a conductor that helps to establish electrical contact with a non-metallic part of the circuit. According to the general definition, an electrode is a substance that helps in electricity conduction wherein the electric current either leaves or enters the non-metallic medium such as an electrolytic cell. Before we learn about the terms cathode and anode, it is important to understand what an electrode is.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
